A change in the magnetic flux in a closed circuit (coil) induces a potential difference.
Law of Faraday:
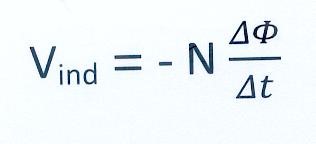
- Vind average induced potential difference in V
- N amount of loops of the coil
- ΔΦ change of magnetic flux in Wb
- Δ t time interval in which change occurs in s
Example

See the figure above.
The area of the turn is 40 cm2
The magnitude of the magnetic induction is 0.020 T
The turn is rotated.
At the moment of the figure the field lines are parallel to the turn.
So the magnetic flux is 0 Wb
After 0.0050 s the turn has rotated 90o . In that situation the magnetic flux is maximal
Determine the average induced potential difference (emf) in this time interval.
Vind =- N ( ΔΦ/Δt)
ΔΦ = Φmax – 0 = B A = 0.020 (40 x 10-4)= 8.0 x 10-5 Wb
Vind = 1 (8.0 x 10-5)/0.0050 = 1.6 x 10-2 V
An induction current is produced when A is connected to B
The resistance of the circuit is 0.20 Ω

Uind = Iind R
1.6 x 10-2 = Iind 0.20
Iind = 8.0 x 10-2 A